As The Mobile Indian had reported earlier, a security solution provider has now highlighted that many applications, especially the free ones, sending malwares to Android devices in the disguise of apps.
Lookout mobile security, the security solution provider, has identified 32 such malicious applications of four different App developers which have now been taken down by Google Play.
As per Lookout, the malicious apps used the ‘Ad networks’, which is otherwise used by app developers to earn revenue in order to make their apps available for free, to send malwares to the Android devices.
The working of the malware Ad network is simple: as and when an application is pushed for verification and publication on Google Play, the application showcases ads and just a day after the ad network starts pushing malware on to installed devices through applications.
This makes it easier for the malware to pass through the Google Play verification process which has been strengthened to avoid suspicious applications.
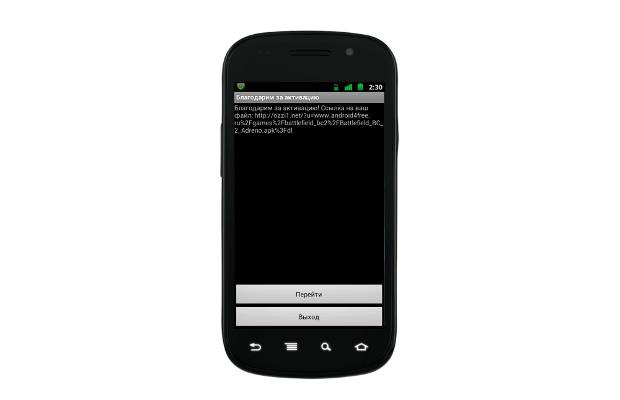
Lookout has found one such ad network, called Badnews, which was found to be pushing a well-known malicious application known as AlphaSMS. The AlphaSMS application poses as an app downloader/installer but instead charges premium SMS. It then redirects the user to a website that contains additional potentially malicious applications to download.
Badnews has the ability to send fake news messages, prompt users to install applications and sends sensitive information such as the phone number and device ID to its Command and Control (C&C) server. BadNews uses its ability to display fake news messages in order to push out other types of monetisation malware and promote affiliated apps.